Explore
Data Exploration
General Resources
Overview
Explanation of the HMS LINCS strategy for data collection and release.
HMS LINCS Database
A public resource for browsing, searching, and downloading HMS LINCS datasets and information about experimental reagents.
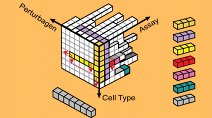
Breast Cancer Browser
The HMS LINCS Breast Cancer Browser is an online portal that provides interactive visualizations of datasets and related information of significant interest to researchers studying breast cancer biology, drug response, and drug polypharmacology.
GR Browser
The GR Browser is an online tool for learning about growth rate inhibition metrics, calculating growth rate inhibition metrics from your own data, and browsing LINCS dose-response datasets.
Publication & Project Summaries
Encoding growth factor identity in the temporal dynamics of a transcription factor under combinatorial regulation
Sampattavanich et al (2018) Cell Systems
Translocation by human FOXO3 is pulsatile rather than oscillatory and subject to combinatorial control by the ERK and Akt pathways. As a result, FOXO3 dynamics can encode the identities and concentrations of diverse extracellular growth factors. Explore time-lapse microscopy videos, raw image data, and single-cell metrics.
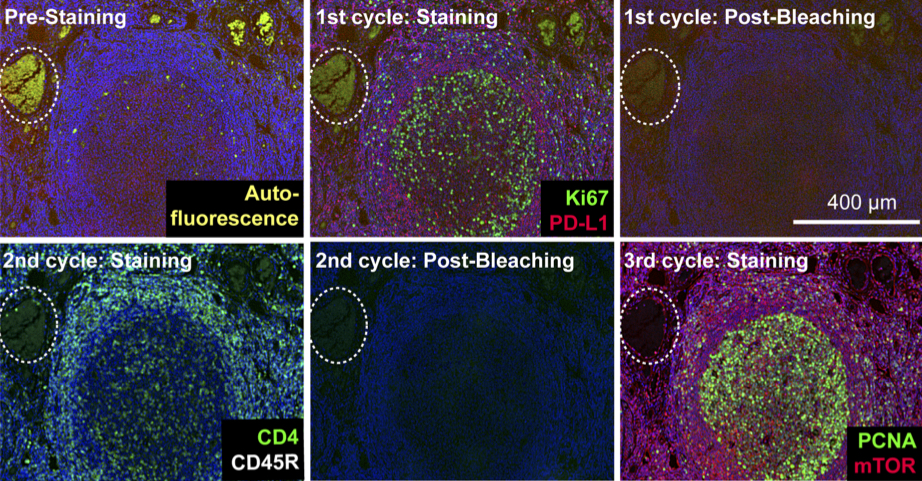
Highly multiplexed immunofluorescence imaging of human tissues and tumors using t-CyCIF and conventional optical microscopes
Lin et al (2018) bioRxiv
Tissue-based cyclic immunofluorescent microscopy (t-CyCIF) is a simple method for generating highly multiplexed optical images from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue samples routinely used for histopathological diagnosis of human disease.
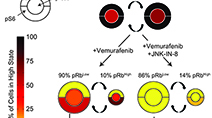
Adaptive resistance of melanoma cells to RAF inhibition via reversible induction of a slowly dividing de-differentiated state
Fallahi-Sichani et al (2017) Molecular Systems Biology
Single-cell imaging, transcriptional profiling, and biochemical profiling of the responses of BRAFV600E melanoma cells to Vemurafenib uncovered a slowly dividing, de-differentiated cell state that is associated with drug resistance but that is inhibitable by novel drug combinations.
Neutral Loss Is a Very Common Occurrence in Phosphotyrosine-Containing Peptides Labeled with Isobaric Tags
Everley et al (2017) Journal of Proteome Research
By characterizing trends in neutral loss and immonium ion formation during mass spectrometry analysis of phosphotyrosine-containing peptide samples, a set of features was identified that can inform improved method development and supplement site localization algorithms for the analysis of isobarically labelled peptides.
A Strategy to Combine Sample Multiplexing with Targeted Proteomics Assays for High-Throughput Protein Signature Characterization
Erickson et al (2017) Molecular Cell
A new targeted mass spectrometry strategy called TOMAHAQ leverages advances in MS3 analysis of reporter ions to enable 10-plex sample multiplexing with accurate quantification directly from proteolyzed cell lysates.
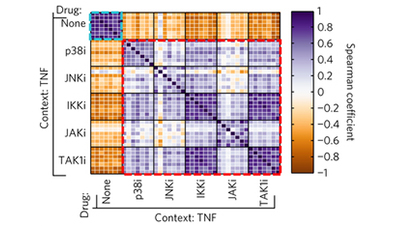
Profiling drugs for rheumatoid arthritis that inhibit synovial fibroblast activation
Jones et al (2017) Nature Chemical Biology
In the context of rheumatoid arthritis, multiple kinase inhibitors partially block ligand-dependent synovial fibroblast activation and proinflammatory cytokine secretion into the synovial fluid, but the TAK1 inhibitor 5ZO is unique among the inhibitors tested in its ligand-independent efficacy across a panel of synovial fibroblasts isolated from RA patients.
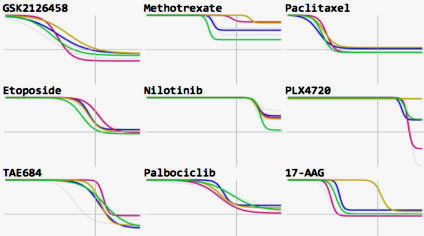
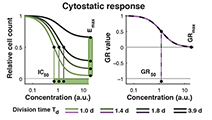
Growth rate inhibition metrics correct for confounders in measuring sensitivity to cancer drugs
Hafner, Niepel et al (2016) Nature Methods
In contrast to conventional metrics for drug response such as IC50 or Emax, growth rate inhibition (GR) metrics are insensitive to division number and provide a more robust measure of the effects of perturbagens on dividing cells.
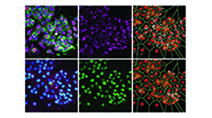
Highly multiplexed imaging of single cells using CycIF, a high-throughput cyclic immunofluorescence method
Lin et al (2015) Nature Communications
CycIF is a high-throughput cyclic immunofluorescence method that uses public domain chemistry and existing instruments to enable low-cost, high-dimensionality imaging assays at the single-cell level.
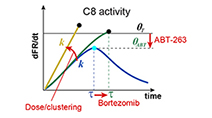
Fractional killing arises from cell-to-cell variability in overcoming a caspase activity threshold
Roux et al (2015) Molecular Systems Biology
Non-genetic cell-to-cell variability results in fractional killing by TRAIL and therapeutic antibody agonists, limiting their effectiveness as anti-cancer drugs. A simple model of initiator caspase dynamics reveals a threshold in caspase activity that separates dying and surviving cells.
Systematic analysis of BRAFV600E melanomas reveals a role for JNK/c-Jun pathway in adaptive resistance to drug-induced apoptosis
Fallahi-Sichani et al (2015) Molecular Systems Biology
Adaptive responses to RAF/MEK inhibitors can limit therapeutic success. We analyzed this adaptive response systematically across a panel of BRAFV600E melanoma lines and revealed a role for cell-to-cell variability induced by the JNK/c-Jun pathway and other factors in adaptive drug resistance.
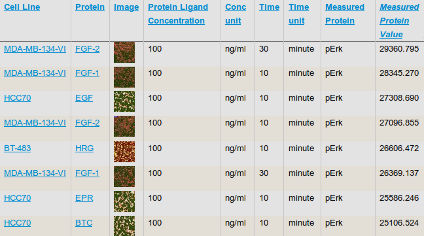
Analysis of growth factor signaling in genetically diverse breast cancer lines
Niepel et al (2014) BMC Biology
Growth factor signaling is a key determinant of cellular behavior in normal and diseased tissue. Here, we generated a systematic dataset looking at the variance of signaling responses across the ICBP43 panel of breast cancer lines and identified potential molecular underpinnings of these responses.
Discovering causal pathways linking genomic events to transcriptional states using Tied Diffusion Through Interacting Events (TieDIE)
Paull et al (2013) Bioinformatics
Tied Diffusion Through Interacting Events (TieDIE) is a novel tool for discovering causal pathways linking genomic events to transcriptional states.
Profiles of Basal and Stimulated Receptor Signaling Networks Predict Drug Response in Breast Cancer Lines
Niepel et al (2013) Science Signaling
Profiling the levels and responsiveness of receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) to diverse growth factors and cytokines across libraries of cancer cell lines makes it possible to predict responsiveness to targeted therapeutics. Analysis of the predictors reveals key protein factors involved in drug sensitivity.
Metrics other than potency reveal systematic variation in responses to cancer drugs
Fallahi-Sichani et al (2013) Nature Chemical Biology
A multi-parametric analysis of a systematic set of dose-response measurements across >50 cell lines to 64 anticancer drugs reveals the extent of variability in maximal effect and slope. Non-canonical behavior appears to arise from cell-to-cell variability.
Differential Determinants of Cancer Cell Insensitivity to Antimitotic Drugs Discriminated by a One-Step Cell Imaging Assay
Tang et al (2013) Journal of Biomolecular Screening
A one-step, no-wash imaging assay that uses three dyes to stain living cells for mitotic and apoptotic state discriminates alternative mechanisms of compromised drug sensitivity.
Mass Spectrometry Based Method to Increase Throughput for Kinome Analyses Using ATP Probes
McAllister et al (2013) Analytical Chemistry
Combination of ActivX ATP probe (AAP) affinity reagents with multiplexed isotopic labeling (TMT) enables systematic kinome analysis across up to six samples in a single LC-MS run.
Common Project MCF 10A Datasets
Profiling the human breast cell line MCF 10A is a key component of the NIH LINCS Consortium Common Project. Here we present a list of all HMS LINCS datasets in which MCF 10A cells were assayed.
Single-cell analysis of perturbagen-induced changes in the subcellular morphology of breast cancer cells
Mills et al (unpublished)
Kinase inhibitors are important candidates for targeted therapy for breast cancer. Browse and download this live-cell imaging dataset assessing subcellular morphology changes in 1.6 million individual cells across 6 breast cancer and non-tumorigenic cell lines treated with a panel of 105 kinase inhibitors.
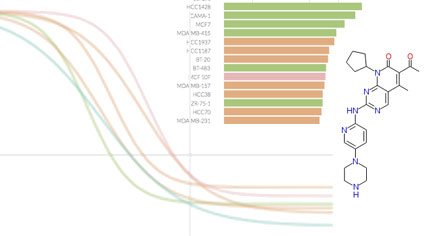
Inhibitor Target Space Studies
KINOMEscan data on kinase inhibitors as perturbagens
KINOMEscan is a biochemical kinase profiling assay that measures inhibitor polypharmacology using ~440 purified kinases. To date, ~150 compounds from the HMS LINCS collection have been profiled using this method.
KiNativ data on kinase inhibitors as perturbagens
KiNativ is a biochemical kinase profiling assay that measures inhibitor polypharmacology in cell lysates. To date, ~25 compounds from the HMS LINCS collection have been profiled using this method.
Experimental & Analytical Methods
Neutral Loss Is a Very Common Occurrence in Phosphotyrosine-Containing Peptides Labeled with Isobaric Tags
Everley et al (2017) Journal of Proteome Research
By characterizing trends in neutral loss and immonium ion formation during mass spectrometry analysis of phosphotyrosine-containing peptide samples, a set of features was identified that can inform improved method development and supplement site localization algorithms for the analysis of isobarically labelled peptides.
A Strategy to Combine Sample Multiplexing with Targeted Proteomics Assays for High-Throughput Protein Signature Characterization
Erickson et al (2017) Molecular Cell
A new targeted mass spectrometry strategy called TOMAHAQ leverages advances in MS3 analysis of reporter ions to enable 10-plex sample multiplexing with accurate quantification directly from proteolyzed cell lysates.
Growth rate inhibition metrics correct for confounders in measuring sensitivity to cancer drugs
Hafner, Niepel et al (2016) Nature Methods
In contrast to conventional metrics for drug response such as IC50 or Emax, growth rate inhibition (GR) metrics are insensitive to division number and provide a more robust measure of the effects of perturbagens on dividing cells.
Highly multiplexed imaging of single cells using CycIF, a high-throughput cyclic immunofluorescence method
Lin et al (2015) Nature Communications; Lin et al (2016) Current Protocols in Chemical Biology
CycIF is a high-throughput cyclic immunofluorescence method that uses public domain chemistry and existing instruments to enable low-cost, high-dimensionality imaging assays at the single-cell level.
Differential Determinants of Cancer Cell Insensitivity to Antimitotic Drugs Discriminated by a One-Step Cell Imaging Assay
Tang et al (2013) Journal of Biomolecular Screening; Tang (2014) Current Protocols in Chemical Biology
A one-step, no-wash imaging assay that uses three dyes to stain living cells for mitotic and apoptotic state discriminates alternative mechanisms of compromised drug sensitivity.
Mass Spectrometry Based Method to Increase Throughput for Kinome Analyses Using ATP Probes
McAllister et al (2013) Analytical Chemistry
Combination of ActivX ATP probe (AAP) affinity reagents with multiplexed isotopic labeling (TMT) enables systematic kinome analysis across up to six samples in a single LC-MS run.